Reconstructive Surgeries
Reconstructive Surgeries
Description
Reconstructive surgeries are a type of surgery aimed at repairing, restoring, or improving the function and
appearance of body parts affected by injury, disease, congenital conditions, or deformities.
Unlike cosmetic surgery, which focuses on enhancing appearance based on aesthetic preferences,
reconstructive surgery is primarily
concerned with restoring normal function and appearance, often to address issues that impact quality of life.
Following procedures we follow to cure through reconstructive surgeries:-
- Flaps
- Skin Grafting
- Minor Burns
- Brachial Plexus Surgery
- Foot & wrist drop
- Post Burn Contracture
- Keloid Hypertrophic scar
- Non healing wound
Flaps
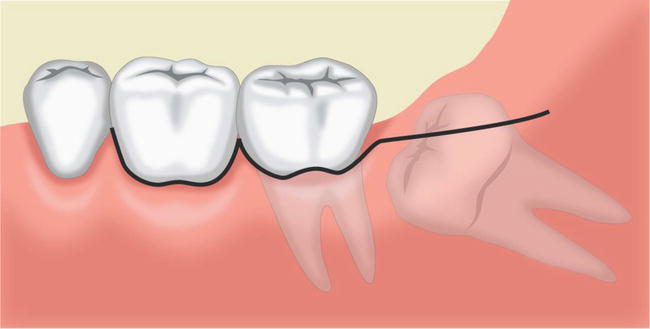
Flaps in surgery refer to a type of tissue transfer used to repair or reconstruct areas of the body affected by injury, disease, or surgical removal. Unlike skin grafts, which involve transferring only the outer layer of skin (epidermis and sometimes part of the dermis), flaps involve transferring a section of tissue that includes not just skin but also underlying structures such as fat, muscle, or even bone. The transferred tissue remains attached to its original blood supply, allowing it to retain its viability and function in the new location.
Skin grafting

Skin grafting is a surgical procedure used to replace damaged or missing skin with healthy skin taken from another part of the body (the donor site) or from a donor. This technique is commonly employed to treat wounds, burns, ulcers, and skin loss due to various conditions. The primary goal is to restore skin integrity, promote healing, and improve functional and aesthetic outcomes.
minor burns
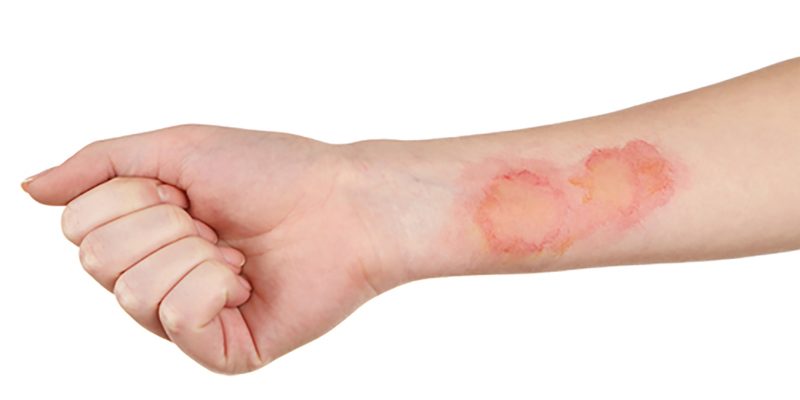
A minor burn is a burn injury that affects only the superficial layers of the skin and does not require extensive medical intervention. Minor burns are generally classified as first-degree burns or, in some cases, small second-degree burns. They are usually less severe than more significant burns and can often be treated effectively with home care.
Brachial Plexus Surgery
Brachial Plexus Surgery refers to surgical interventions aimed at repairing or reconstructing the brachial plexus, a network of nerves originating from the cervical spine (C5 to C8) and upper thoracic spine (T1) that controls the movement and sensation of the shoulder, arm, and hand. Damage to the brachial plexus can result in various functional impairments in the upper limb, including weakness, paralysis, or loss of sensation.
Foot & wrist drop
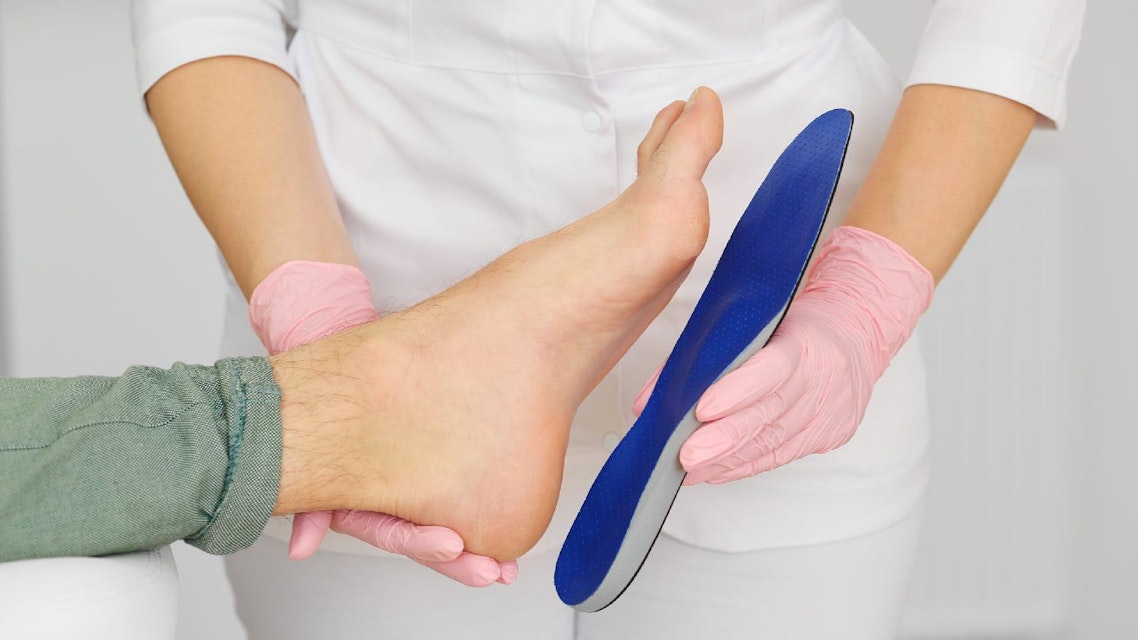
Foot drop and wrist drop are conditions resulting from nerve dysfunction or damage that significantly affect movement and daily activities. Foot drop typically involves difficulty lifting the foot, while wrist drop involves an inability to extend the wrist and fingers. Treatment for both conditions often involves a combination of orthotic devices, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention, depending on the underlying cause and severity.
Post Burn Contracture

Post-burn contracture is a condition that occurs when a burn injury causes the skin and underlying tissues to contract, resulting in restricted movement and potential deformity. This happens due to the healing process of the burn, where scar tissue forms and pulls the surrounding skin and tissues inward. It commonly affects the area around the burn but can impact any part of the body depending on the location and severity of the injury.
Keloid Hypertrophic scar
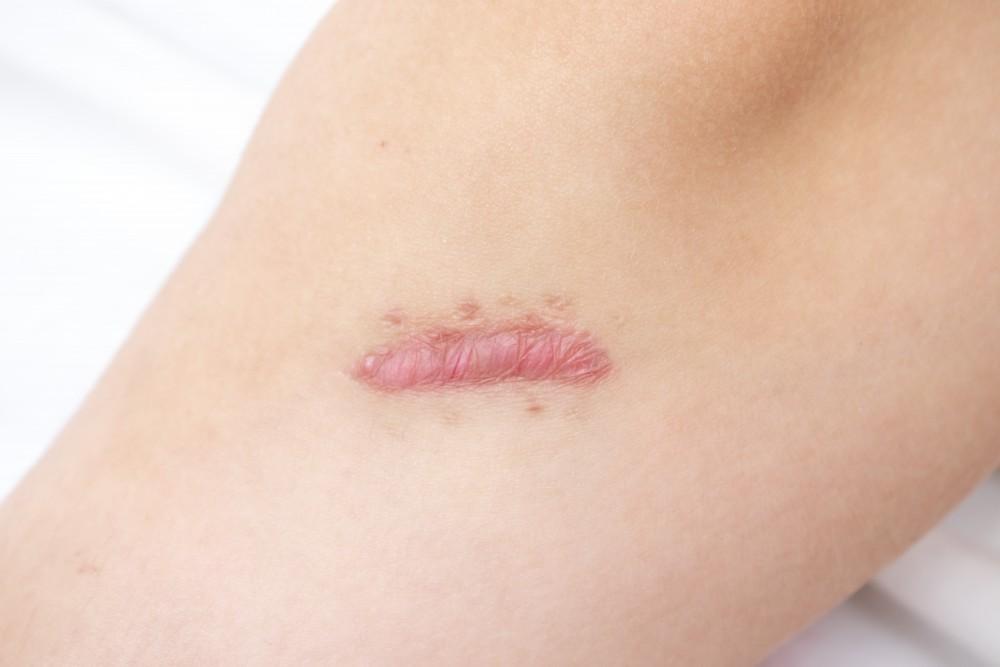
Keloid and hypertrophic scars are two types of abnormal scarring that can result from excessive collagen production. Keloids extend beyond the original wound and continue to grow, while hypertrophic scars remain within the wound’s boundaries and may improve over time. Treatment for both types of scars involves a combination of medical and therapeutic interventions to reduce their appearance and improve patient comfort.
Non healing wound
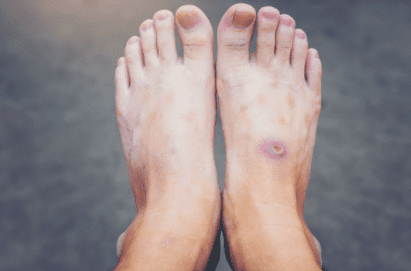
A non-healing wound is a wound that fails to progress through the normal stages of healing and does not close or improve over time. Such wounds persist for an extended period, often beyond the typical healing time expected for similar injuries or surgical sites. Non-healing wounds can be challenging to manage and may require specialized treatment.
© Copyright 2024 All Rights Reserved | Website Managed By Nishar India or Call Us +91 8839946717.
